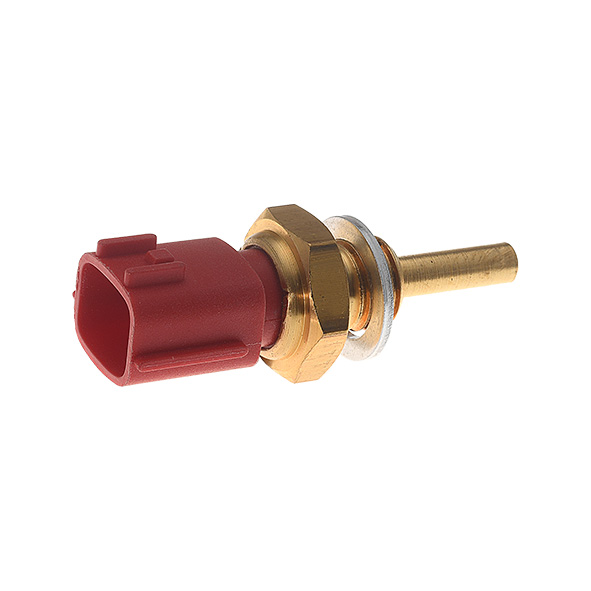
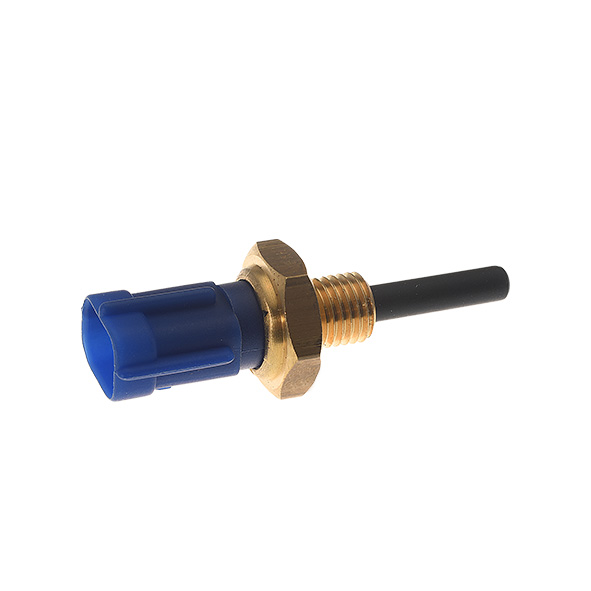
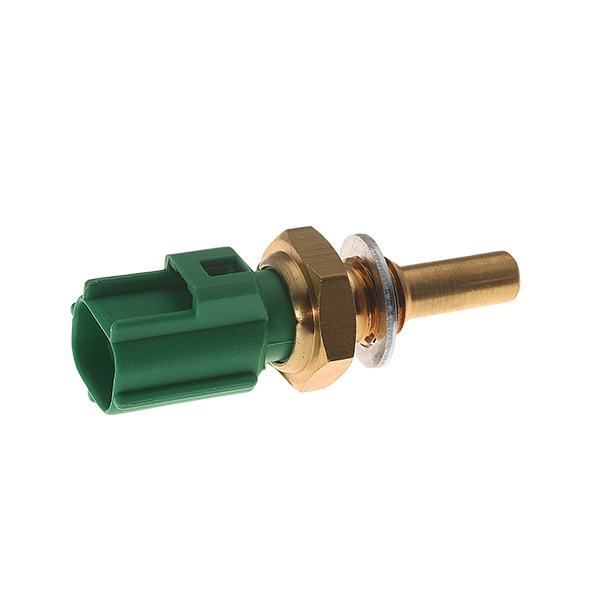
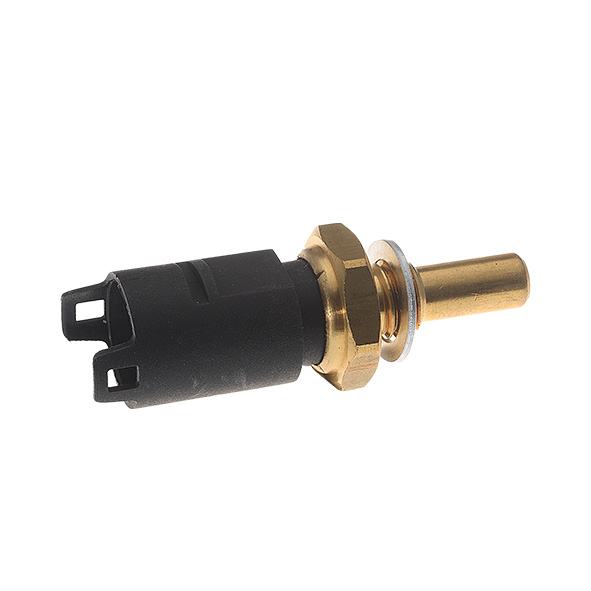
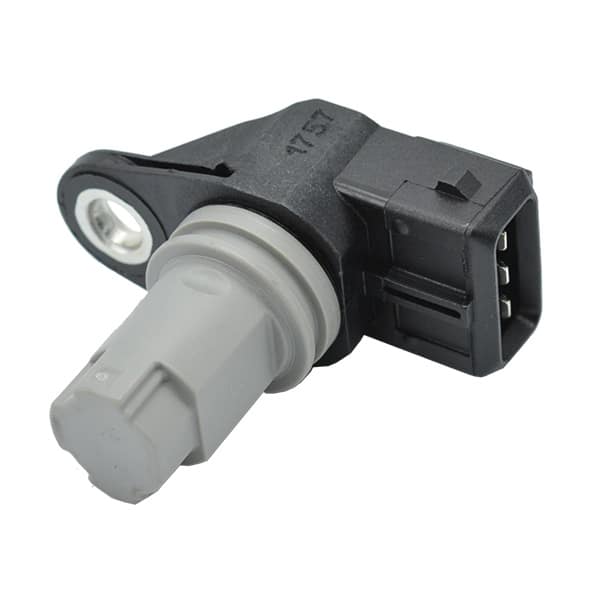
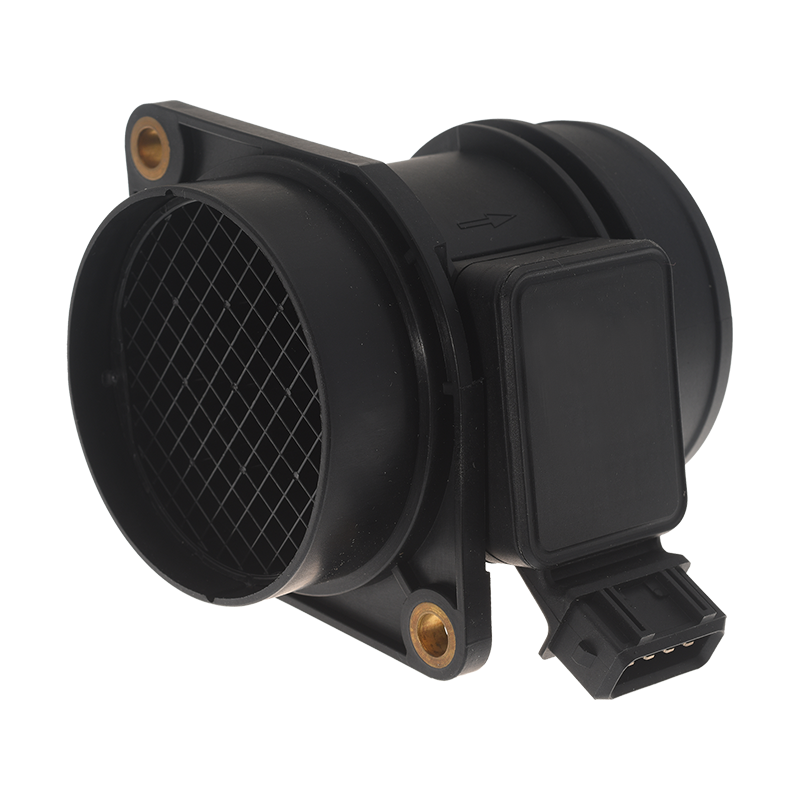
First of all, we strongly advise you to visually check the temperature sensor; i.e., the metal body of the sensor (visible dents, cracks or any kind of blow that could have damaged it), the connector (visible loose connections, melted or cracked wires) and its wiring (ensure it is not damaged or broken).
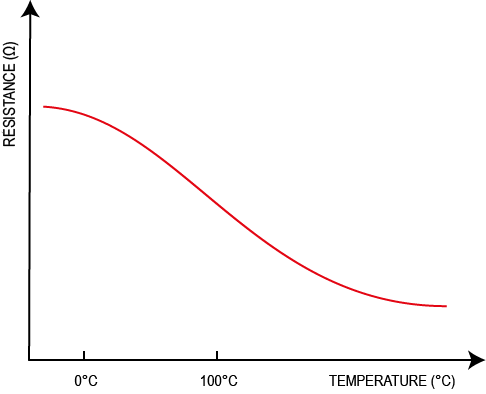
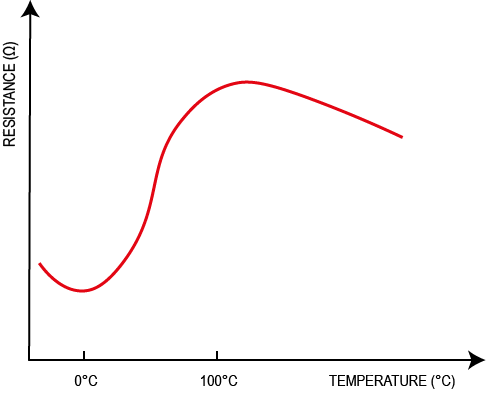
Secondly, you can test your sensor’s correct functioning by checking its resistance. By plugging the measuring tool into the sensor connector and heating the side where the probe is located, you can check whether the resistance fluctuates. However, you will need to make sure that you have set the multimeter to 20M Ω, and that you know which technology your sensor uses (NTC or PTC type – see “Technologies” section). Depending on the sensor type, either the resistance will increase when the temperature increases (PTC), or conversely it will decrease when the temperature increases (NTC).
If the above tests are not conclusive, then it would appear that you need to replace your vehicle’s temperature sensor.