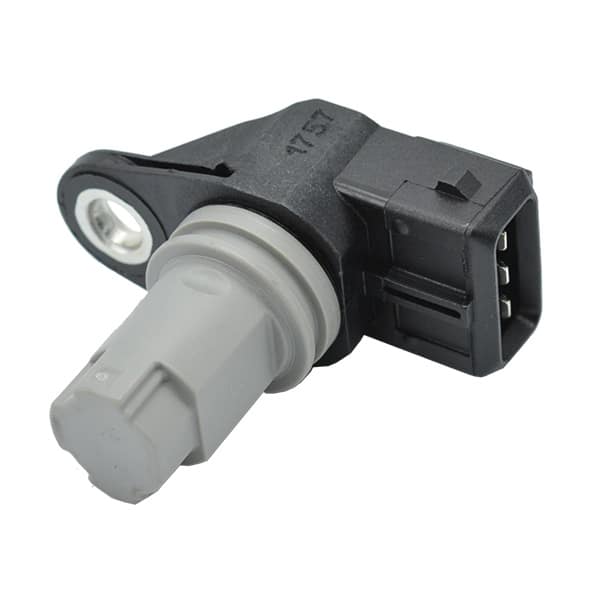
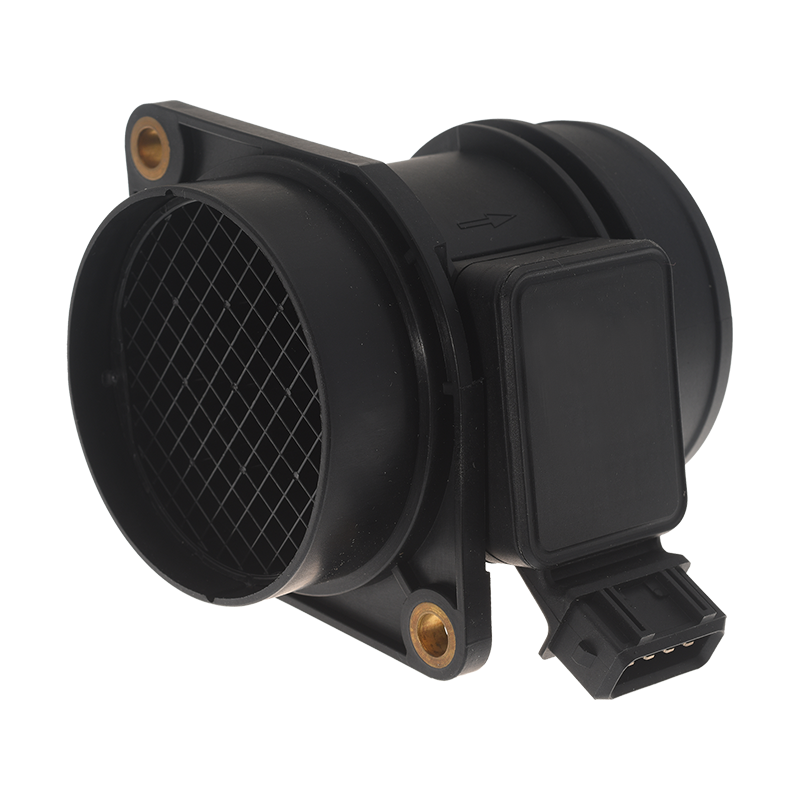
When the accelerator pedal position sensor malfunctions, the signal transmitted to the engine control unit may be erratic or absent, causing noticeable malfunctions while driving. The vehicle may exhibit slow or irregular throttle response, with jerks during acceleration, loss of power, or activation of a degraded mode that limits engine speed to ensure safety. The engine warning light may also come on, accompanied by warning messages on the dashboard, and the engine speed may vary unexpectedly or even remain at idle despite pressing the pedal. These anomalies reflect poor transmission of the driver’s intention to the ECU and require prompt verification in order to maintain responsiveness, safety and driving comfort.