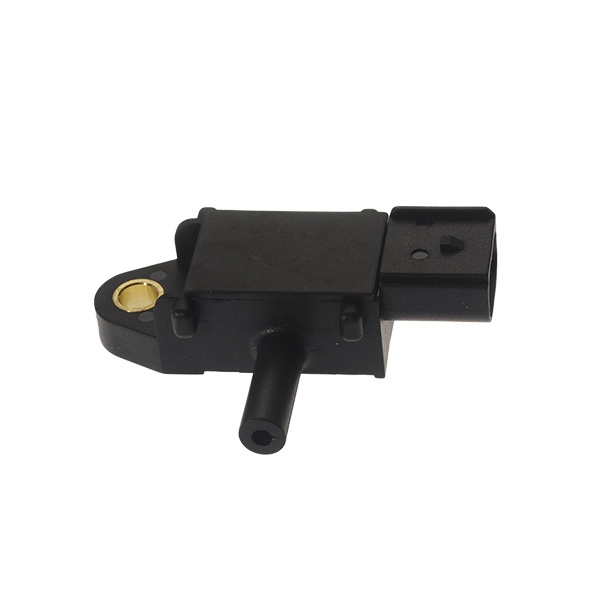
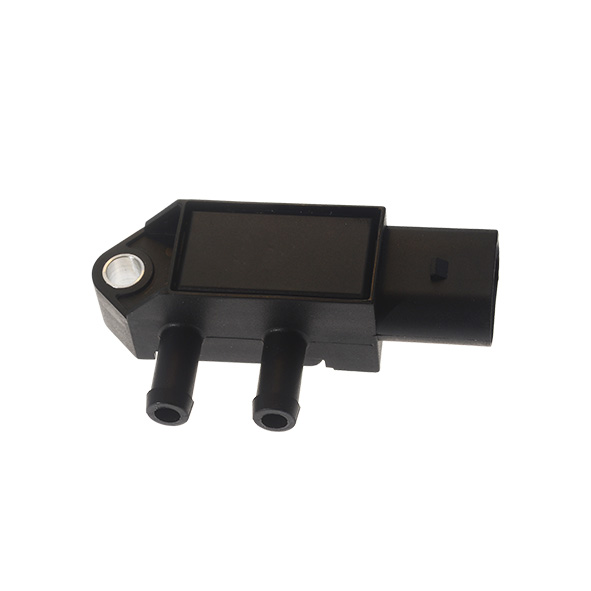
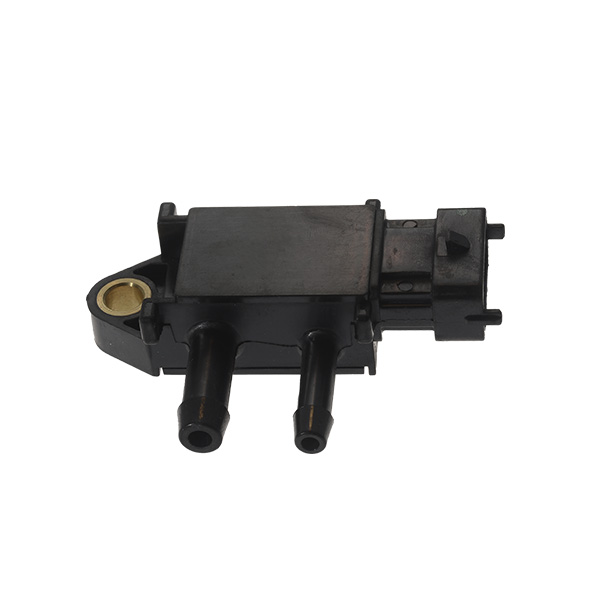
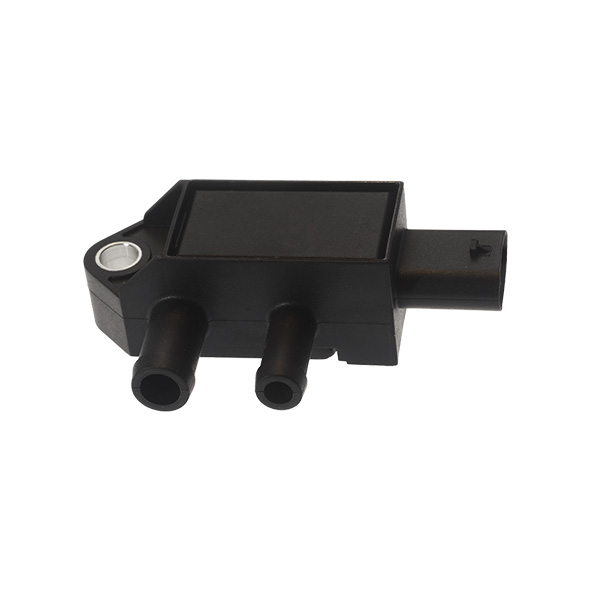
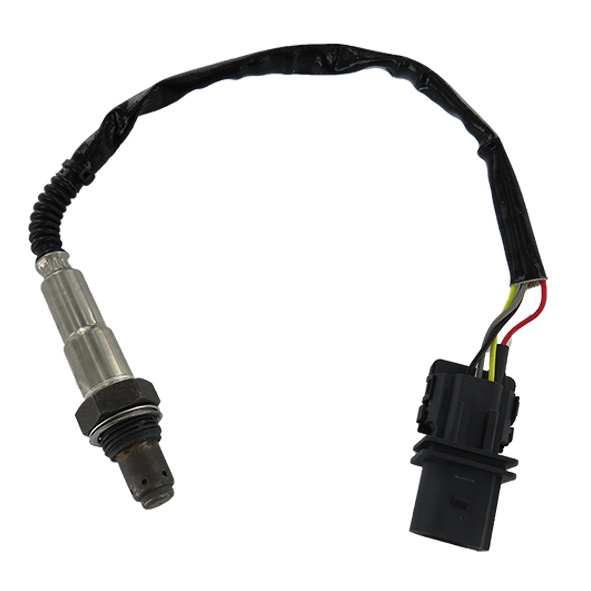
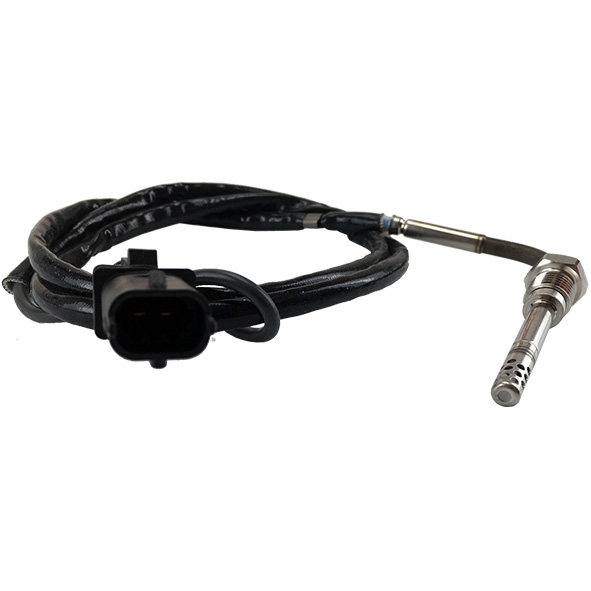
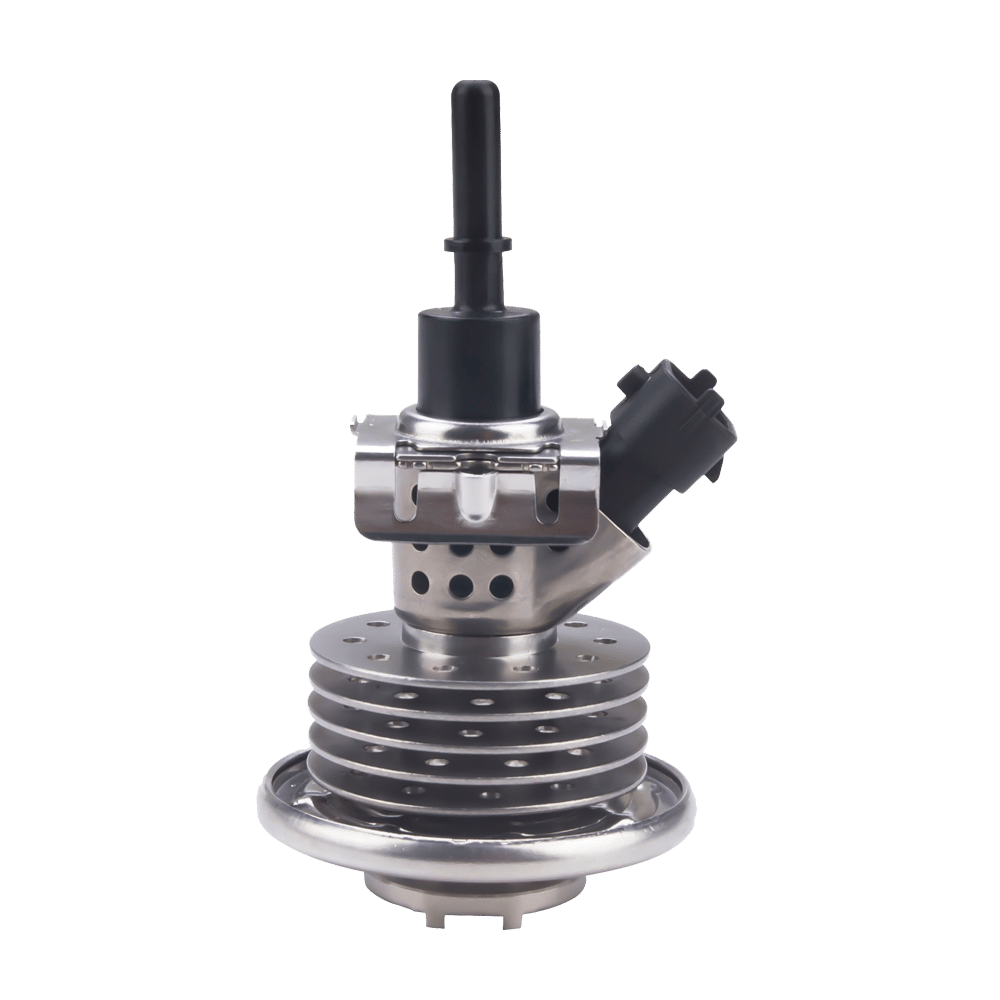
First of all, you should visually check the differential pressure sensor; i.e., the sensor itself (presence of dirt), the connector (presence of oxidation) and its pipes (neither broken nor clogged).
It is also possible to check the contact spacing with a male terminal (resistance to insertion). Using a voltmeter, check the 5V supply and the sensor ground. Also measure 5V on the signal wire with the sensor disconnected. By shunting the signal wire and the ground, the voltage drops to 0.
After disconnecting the particulate filter’s two pressure taps, measure the output signal with an oscilloscope and view the differential pressure value (0 hPa). Blow into the upstream pressure port: no change in voltage or differential pressure. After changing the differential pressure sensor, perform the test again. Measure the output signal at 0 hPa (higher signal). By blowing into the orifice, the signal and the differential pressure increase.
If the above tests are not conclusive, you need to replace your vehicle’s differential pressure sensor.